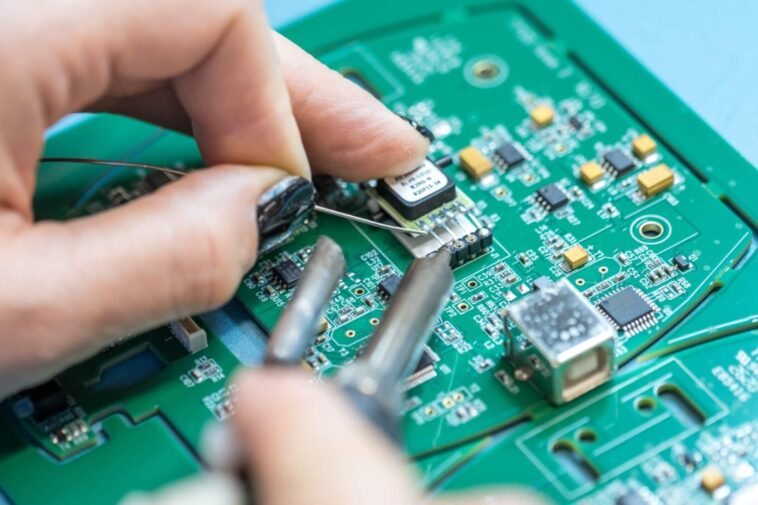
The electronics that power our everyday lives have become smaller, smarter and more sophisticated. Behind this progress lies one essential process that turns concept into reality: PCB assembly. From consumer gadgets and household appliances to advanced industrial systems, PCB assembly is the bridge between a designed circuit board and a fully functioning electronic product.
Whether you are part of an engineering team, a manufacturer or a business exploring outsourced production, understanding how PCB assembly works will help you make better decisions about product development, costs and quality. This guide explores the process, the technology behind it and the reasons why professional assembly is vital.
What Is PCB Assembly?
PCB assembly is the process of attaching electronic components onto a bare Printed Circuit Board. Although a PCB contains copper pathways and pads for electrical connections, it cannot function on its own. It requires components such as transistors, capacitors, ICs, resistors and connectors to be accurately mounted and soldered in place.
The complexity of this process varies depending on the design, component types and end-use requirements. Precision is crucial, as even the smallest misalignment or soldering issue can impact performance, safety or product lifespan.
For more information, you can visit PCB Assembly.
Surface Mount Technology
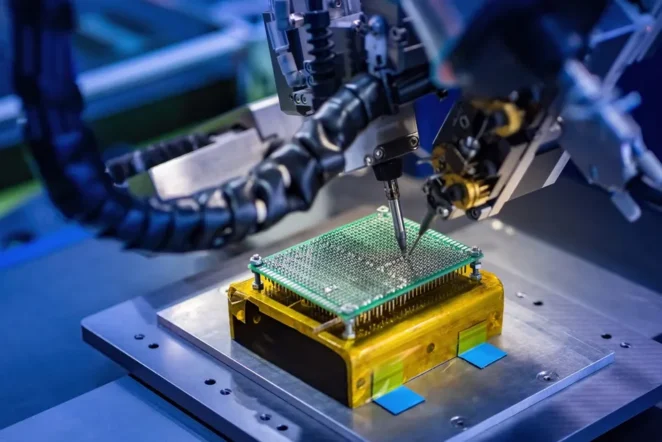
Surface Mount Technology transformed the electronics industry by enabling manufacturers to place components directly onto the board surface without using drilled holes. With SMT, solder paste is first printed onto the board using a stencil, and high-speed pick-and-place machines position each component with remarkable accuracy.
Once the components are placed, the board goes through a reflow oven. This controlled heating process melts the solder paste and forms strong, reliable joints. SMT supports miniaturisation, faster production cycles and higher component density, making it suitable for most modern electronics.
Through-Hole Technology
Although SMT dominates the majority of modern manufacturing, through-hole technology still plays a vital role. Through-hole components have leads that pass through pre-drilled holes in the PCB and are soldered either by machine or by hand.
This method provides superior mechanical strength compared with surface mounting. As a result, through-hole components are often used in applications where durability is essential, such as industrial machinery, automotive systems, and aerospace electronics. Large components such as transformers and connectors also rely on through-hole mounting due to their size and physical demands.
The PCB Assembly Workflow
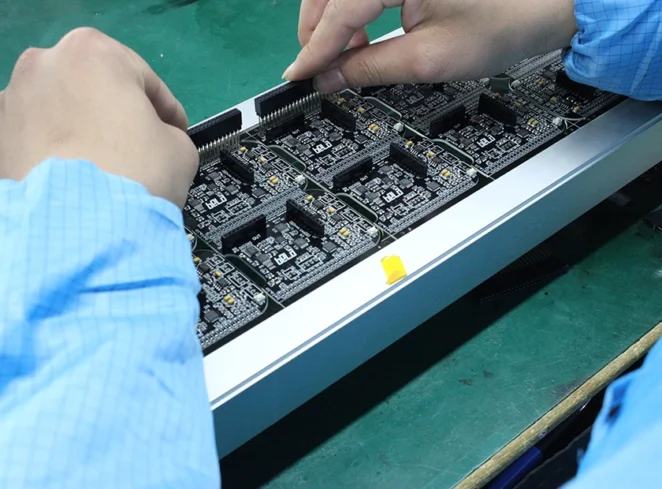

PCB assembly is a multi-stage process that requires precision at every step. The typical workflow involves:
- Solder paste printing ─ A stainless steel stencil ensures solder paste is applied accurately to each pad on the PCB. This guarantees the correct amount of solder for reliable joints.
- Pick-and-place assembly ─ Automated equipment places components onto the board at high speed. Modern machines can place thousands of components per minute while maintaining extreme accuracy.
- Reflow soldering ─ During SMT assembly, the populated board enters a reflow oven. Temperature is gradually increased to melt the solder and then lowered to solidify it, securing each component in place.
- Wave or hand soldering ─ For through-hole components, wave soldering is often used. The underside of the board passes over a wave of molten solder that bonds the leads to the pads. More intricate assemblies may require skilled hand soldering.
- Inspection and testing ─ Quality control is at the heart of PCB assembly. Automated Optical Inspection checks for misplaced components, solder issues or incorrect polarity. X-ray inspection may be used on complex joints such as BGAs. Final functional testing ensures the assembled PCB performs correctly before shipping.
Why Professional PCB Assembly Matters
Outsourcing PCB assembly to a reliable provider offers several valuable advantages:
Consistency and Accuracy
Automated machinery reduces human error and ensures components are placed and soldered with consistent precision. This is especially important for high-density or high-performance boards.
Cost Efficiency
Professional assembly partners optimise workflow, minimise waste, and use automated equipment to reduce production costs. This enables businesses to scale without investing in expensive manufacturing tools.
Faster Turnaround
Whether producing prototypes or large production runs, experienced assembly facilities can deliver faster results through optimised processes and advanced machinery.
Technical Expertise
An experienced provider will also offer design for manufacturability guidance. This helps identify potential issues early, streamlines assembly, and reduces the risk of faults.
Quality Assurance
Comprehensive inspection and testing ensure that every board meets performance, safety, and durability standards.
Applications of PCB Assembly Across Industries

PCB assembly supports a wide range of industries, each with unique requirements:
Consumer Electronics
Devices such as smartphones, laptops, and home automation systems require compact, densely populated PCBs with high reliability.
Automotive Technology
From entertainment systems to engine control units, modern vehicles rely on advanced electronics that must withstand heat, vibration, and long-term use.
Industrial and Manufacturing Automation
Robotics, control systems, sensors and factory equipment require robust assemblies that deliver consistent, long-term performance.
Medical Devices
Patient monitoring equipment, imaging technology, and wearable medical products demand precision, cleanliness, and rigorous quality control.
Telecommunications
Network infrastructure, data transmission devices, and wireless communication systems depend on complex PCB assemblies capable of handling high-speed signals.
Final Thoughts
PCB assembly is an essential part of bringing any electronic product to life. From automated SMT processes to durable through-hole techniques, the quality of the assembly directly affects performance, reliability, and product longevity.
Choosing the right assembly partner can significantly improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure consistent results.