Excel is more than just a place to type numbers. It’s a powerful tool that can save time, organize your work, and help you make better decisions.
But to truly get the most out of it, you need to go beyond the basics. That’s where mastering formulas and formatting comes in.
If you’ve already used Excel a bit and want to level up your skills, an excel intermediate course is a great way to do that.
It helps you understand the magic behind those little boxes and how to make your data work for you.
Why Formulas Matter

Formulas in Excel are like tiny calculators built into each cell. They help you do everything from adding up a column to solving complex problems. At the intermediate level, you start to unlock the real power of formulas.
Here are some key ones you’ll learn:
- SUMIF: Add numbers only if certain conditions are met.
- VLOOKUP: Find data across different sheets or tables.
- IF: Make decisions like “If this is true, then do that.”
- TEXT: Format numbers and dates exactly how you want.
- COUNTIF: Count how many times something appears.
- INDEX: Returns a value from a cell based on row and column numbers
- MATCH: Helps find the position of an item in a range
When used together, index and match are powerful alternatives to traditional lookup functions.
Another useful function at this level is IFERROR, which lets you handle errors gracefully. Instead of showing “#DIV/0!”, you can tell Excel to display something friendlier, like “Check input” or “N/A”. This makes your spreadsheets more user-friendly.
With these tools, you don’t just look at numbers—you control them.
The Power of Cell References

One key concept in any Excel intermediate course is cell referencing. Instead of typing the same value again and again, you can tell Excel to use values from other places. There are two main types:
- Relative Reference (like A1): Changes when you copy it to another cell.
- Absolute Reference (like \$A\$1): Stays the same no matter where it’s copied.
You’ll also come across mixed references (like A$1 or $A1), where only the row or column stays fixed. These are especially useful when building templates or setting up dynamic models. Once you grasp these, your formulas will become a lot more adaptable and efficient.
Learning how to use both correctly is a game-changer. It keeps your sheets clean, smart, and easy to update.
Formatting for Clarity
Formulas do the thinking, but formatting does the talking. Good formatting makes your spreadsheet easy to read and understand.
Here are some formatting skills you’ll master:
- Conditional Formatting: Color-code cells based on rules (like highlight anything over \$500).
- Custom Number Formats: Show numbers as currency, percentages, or even symbols.
- Freeze Panes: Keep headers visible while scrolling through long data lists.
- Cell Styles: Apply consistent colors, fonts, and borders quickly.
You’ll also learn about using themes and templates. Themes ensure consistent font and color use across multiple worksheets, which is helpful when creating reports or sharing files with colleagues.
Don’t underestimate the impact of consistent alignment and spacing. Using horizontal and vertical alignment, adjusting column widths, and applying white space strategically makes your work look polished and readable.
These tools make your work look more professional and easier to follow for others.
Tables and Data Management

At the intermediate level, you’ll also start working with Excel Tables. These aren’t just pretty grids—they let you sort, filter, and analyze data with just a few clicks.
You’ll also learn how to:
- Remove duplicates in a list.
- Create dropdown lists using data validation.
- Group rows or columns to keep your data tidy.
Another vital tool is the use of structured references in Excel Tables. Once you turn a range into a Table, your formulas can reference entire columns by name instead of cell range (like =SUM(Table1[Amount])), which makes your work easier to understand.
Data validation can also be expanded with dependent dropdown lists. For example, selecting a country in one cell can automatically populate the next dropdown with only its cities. This brings more interactivity and reliability into your forms.
All of this makes Excel feel less like a spreadsheet and more like a smart assistant.
Building Smarter Spreadsheets
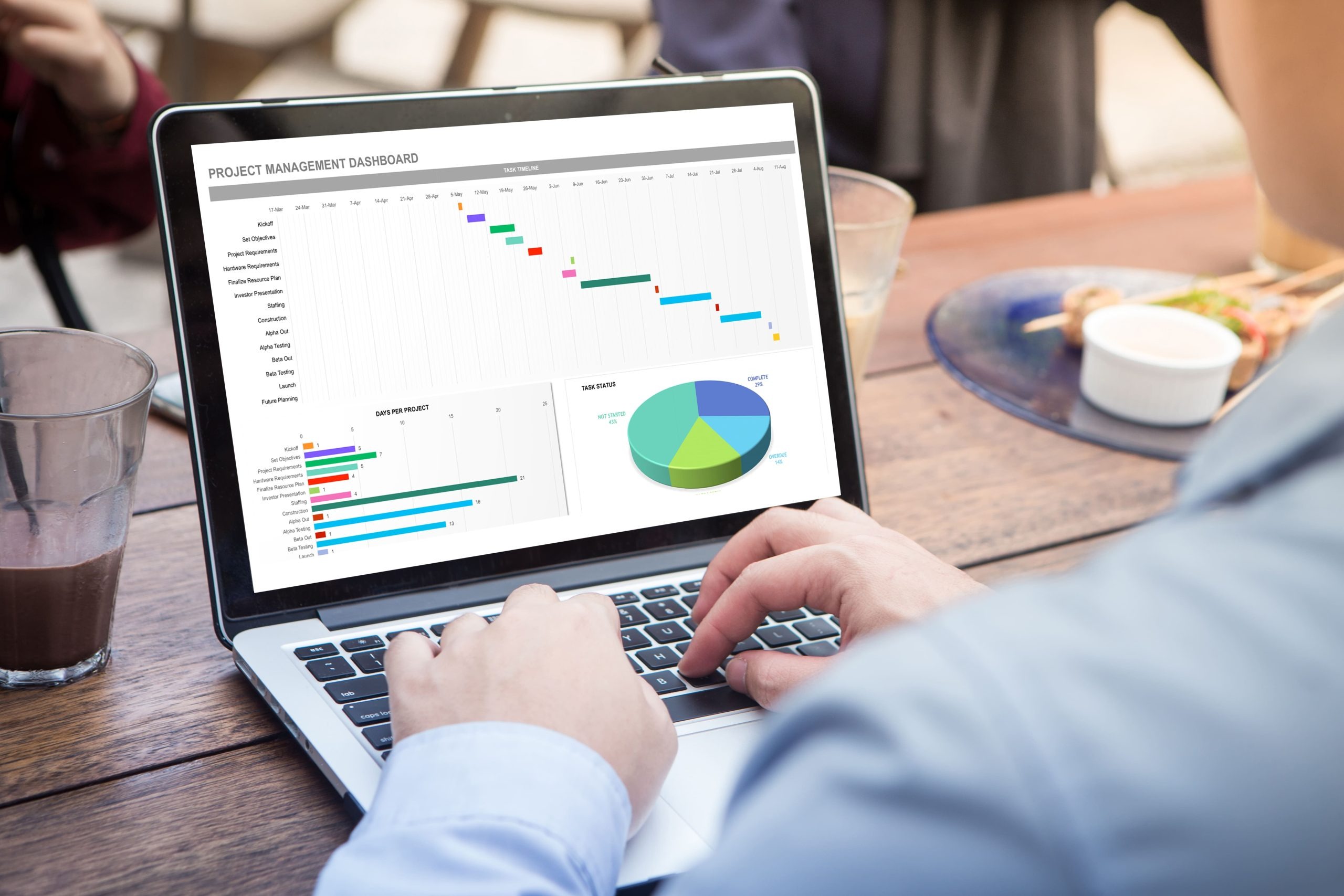
When you combine formulas and formatting, your spreadsheets stop being just files and start becoming tools. You can:
- Automatically update results when numbers change.
- Build dashboards with charts and summaries.
- Use functions together (called nesting) to create custom logic.
An Excel intermediate course teaches you how to build these smarter spreadsheets step-by-step. You don’t need to be a math expert—just someone who wants to work smarter.
You’ll also learn to use named ranges, which let you assign a name to a specific group of cells. Instead of writing =SUM(B2:B10), you can use =SUM(SalesTotal). This makes formulas easier to read and maintain.
PivotTables are another powerful addition at this stage. They allow you to summarize large data sets with just a few clicks, create dynamic reports, and instantly filter or rearrange information. Mastering PivotTables gives you a new level of confidence in handling complex data.
Real-World Uses
Here are just a few ways these skills help in real life:
- At work: Track sales, create reports, or manage budgets.
- At home: Plan vacations, organize home expenses, or track goals.
- At school: Manage project deadlines or analyze survey results.
Even small businesses can benefit by using Excel to automate invoices, employee schedules, or inventory lists. With proper formatting and formulas, these can turn into reliable systems that replace expensive software.
In collaborative settings, these skills help you create files others can use without needing your guidance. A spreadsheet with clear labels, intuitive formulas, and protection on key cells can be a powerful shared resource.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
As you go deeper into Excel, it’s just as important to know what not to do.
- Hardcoding values into formulas: Always reference cells instead. It keeps things flexible and error-free.
- Overusing merged cells: They can mess with sorting and filtering. Instead, use center-across selection.
- Skipping documentation: Add comments or notes to complex formulas so others (or future you) understand them later.
- Not backing up versions: Use “Save As” to keep old versions before major changes.
- Relying only on visuals: Always double-check that your charts reflect accurate and updated data.
Avoiding these habits early helps you become a more reliable and respected Excel user.
Why Keyboard Shortcuts Matter
If you’re still reaching for the mouse every few seconds, you’re losing time. Intermediate users start to lean into Excel’s keyboard shortcuts to speed up everything.
- Ctrl + Shift + L: Toggle filters
- Alt + =: AutoSum
- Ctrl + T: Turn range into Table
- Ctrl + Arrow Keys: Jump to edge of data
- F4: Repeat last action or toggle absolute references
Learning even 5–10 shortcuts that you use often can shave minutes off every task. Over time, that adds up to hours saved.
Ready to Level Up?
If you’re comfortable using Excel but want to unlock its true potential, now is the time to explore an Excel intermediate course. You’ll go from doing things manually to building spreadsheets that almost run themselves.
It’s not about being fancy—it’s about being efficient.
And with the right knowledge, Excel becomes more than just software—it becomes a productivity ally you’ll wonder how you ever lived without.



