Alternative and complementary therapies have grown in popularity recently for a variety of medical ailments. Chelation therapy is one such therapy that has generated interest due to its potential to help treat a number of medical ailments. An in-depth discussion of chelation therapy’s definition, methodology, active ingredients, and potential patient advantages will be provided in this article.
Understanding Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy uses specific chelating chemicals to rid the body of heavy metals and other potentially toxic elements. It is a novel medical procedure. The Greek word “chele,” which means claw, is where the word “chelate” comes from. This phrase accurately reflects how chelating agents work since they behave somewhat like a claw, latching onto and binding with dangerous metals to speed up their removal from the body.
The concept of chelation therapy dates back to the early 20th century and was initially utilized to treat cases of metal poisoning. In contemporary times, the medical community acknowledges the role of chelation therapy not only as an effective treatment for metal toxicity but also as a potential approach to treating certain health conditions.
How Chelation Therapy Works
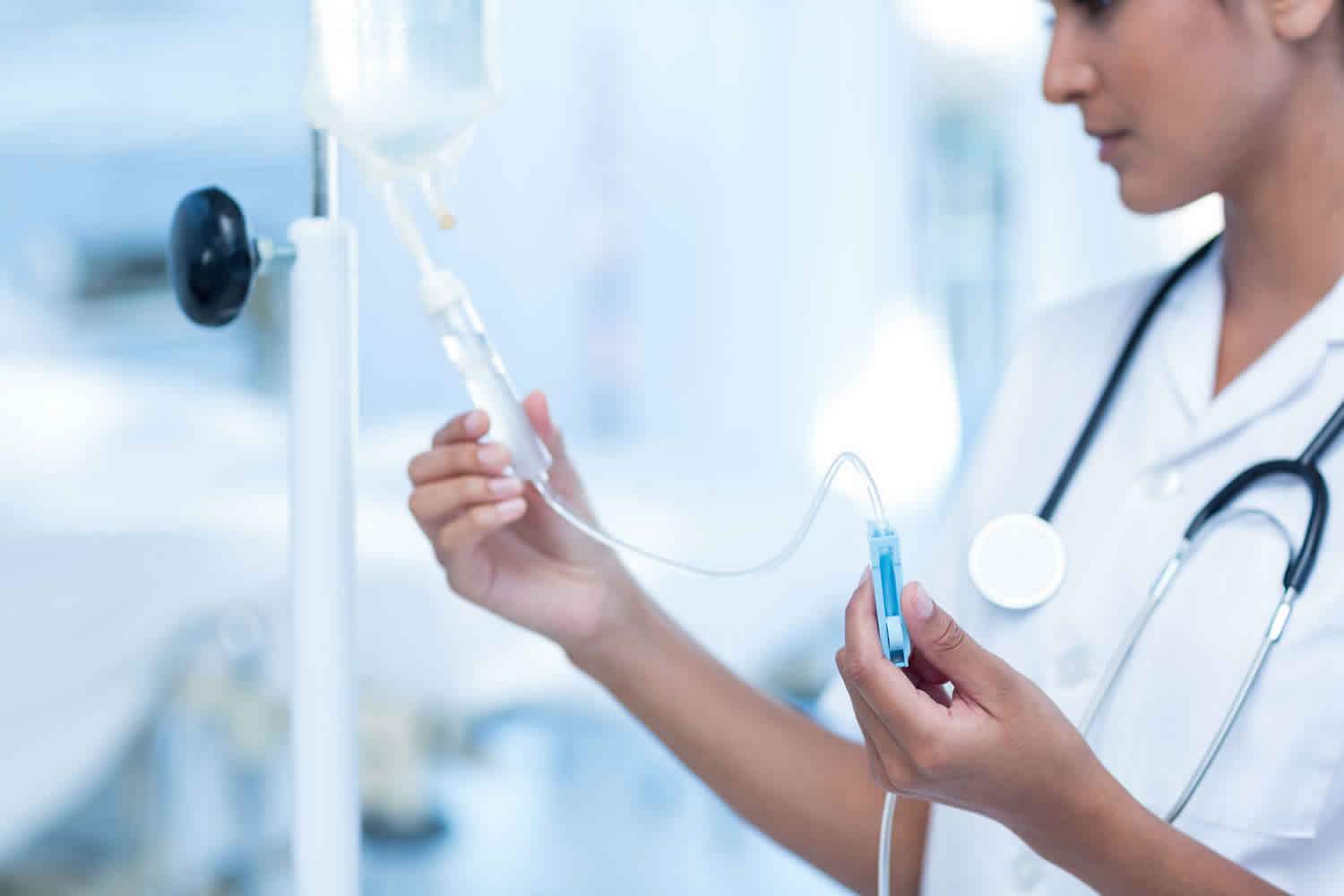
The process of chelation therapy begins with the administration of chelating agents into the body, often delivered via intravenous (IV) infusion. However, in certain circumstances, these agents can also be taken orally or applied topically.
Chelating agents are carefully selected for their unique ability to target and bind specific metals or substances. The resulting complexes are then excreted from the body through natural processes, such as urination or defecation, thereby reducing the levels of the targeted substance in the body.
One of the most commonly used chelating agents is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Recognized for its high affinity for heavy metals, EDTA has proven extremely effective in treating cases of lead, mercury, and cadmium toxicity. Once introduced into the bloodstream, EDTA quickly locates these metals and binds to them, forming a stable compound that the body can safely excrete.
It’s important to note that chelation therapy should always be administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s overall health, the specific metals or substances involved, and the appropriate dosage and administration of chelating agents.
Chelation Therapy Medications
Apart from EDTA, there are other chelating agents that healthcare providers may use for specific metal toxicities. Some of the commonly used medications in chelation therapy include:
EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid)
EDTA is the most widely used chelating agent in chelation therapy. It is administered intravenously and is effective in removing heavy metals from the bloodstream. Besides metal toxicity, EDTA has been explored for its potential benefits in treating cardiovascular diseases, although further research is needed in this area.
DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic Acid)
DMSA is another chelating agent used for treating lead poisoning, particularly in children. It is available in oral form, making it more convenient for pediatric patients who may have difficulties with intravenous treatments.
DMPS (Dimercaptopropane Sulfonate)
DMPS is an effective chelating agent for mercury and arsenic poisoning. It is also available in both oral and intravenous forms.
The Process of Chelation Therapy
Before undergoing chelation therapy, patients undergo a thorough evaluation to assess their metal levels and overall health status. This evaluation helps healthcare providers determine the appropriate chelating agent and treatment plan.
During the procedure, the chelating agent is slowly infused into the patient’s bloodstream through an IV line. The process may take several hours, and the number of sessions required varies depending on the individual’s condition and metal toxicity levels.
Safety and Side Effects of Chelation Therapy
Like any medical procedure, chelation therapy comes with potential side effects. Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, headache, and fatigue. However, severe adverse reactions are rare when administered by trained healthcare professionals.
It is crucial to stress that chelation therapy should only be performed under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider. Self-administered or unsupervised use of chelating agents can lead to serious health risks.
Chelation Therapy Benefits
Treating Heavy Metal Poisoning
The primary and well-established use of chelation therapy is in treating heavy metal poisoning. Exposure to lead, mercury, arsenic, and other toxic metals can occur through various sources, such as contaminated water, food, or industrial exposure. Chelation therapy can help remove these metals from the body and prevent or reduce the associated health risks.
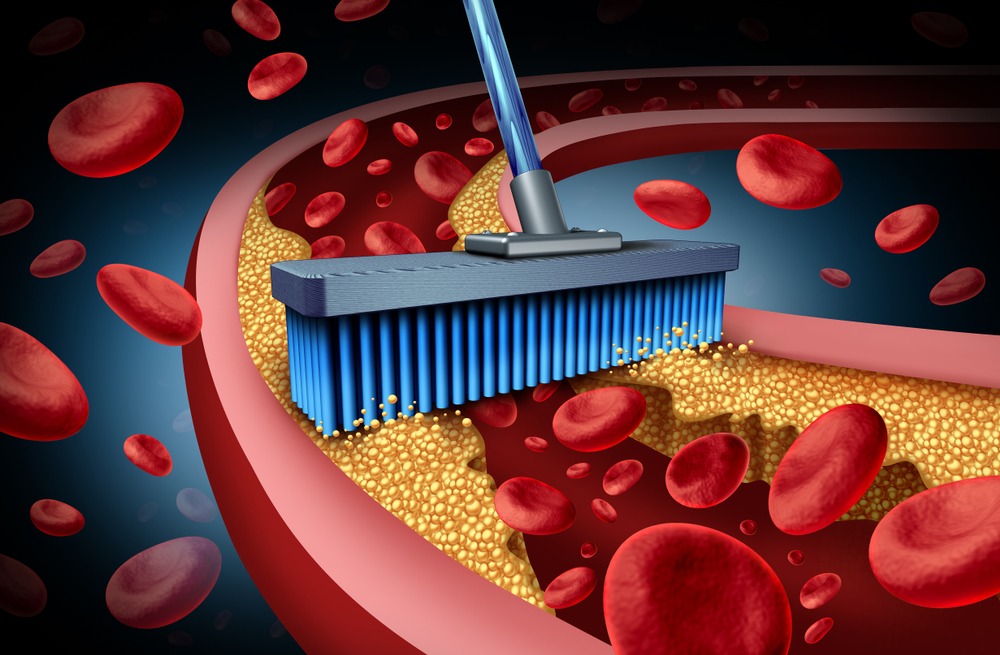
Cardiovascular Health
Chelation therapy has also garnered attention for its potential cardiovascular benefits. Some studies have explored the use of chelation therapy in patients with atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and coronary artery disease. The idea is that chelation therapy might help remove calcium deposits from arterial walls and improve blood flow. However, the evidence in this area is mixed, and more research is needed to establish its efficacy.
Improved Kidney Function in Some Cases
In certain medical conditions, such as thalassemia and hemochromatosis, where excess iron accumulates in the body, chelation therapy can be used to reduce iron levels and improve kidney function.
Controversy and Alternative Uses
Chelation therapy has also been promoted as an alternative treatment for autism and other chronic conditions, and you can find professional providers that offer the ASD test Sydney for accurate diagnosis and support. However, these uses are highly controversial, and there is limited scientific evidence to support their effectiveness. In fact, the American Academy of Pediatrics and other medical organizations caution against using chelation therapy for autism outside of rigorous clinical trials.

Conclusion
Chelation therapy, when administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can be a valuable tool in treating heavy metal poisoning and certain medical conditions associated with metal toxicity. While its use in cardiovascular health and other alternative treatments is still a subject of ongoing research and debate, chelation therapy remains an important treatment option for specific situations.
As with any medical intervention, it is crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and to follow the advice of qualified healthcare providers. Chelation therapy should never be attempted without proper medical supervision, as misuse of chelating agents can lead to serious health consequences. With ongoing research and advancements in medical science, our understanding of chelation therapy may continue to evolve, offering new insights into its potential applications in the future.




